Oxybutynin
Oxybutynin treats overactive bladder. Oxybutynin can cause constipation and blurred vision.
Oxybutynin Overview
Oxybutynin is a prescription medication used to treat overactive bladder. Oxybutynin belongs to a group of drugs called antispasmodics, which help to relax the bladder muscle.
This medication comes in tablet (immediate and extended release forms), gel, liquid (syrup) or transdermal (patch) form, and is taken up to 4 times daily, with or without food. It is also available over-the-counter, in a patch formulation. Do not chew, divide, or break the extended release form of this medication (ditropan XL tablets). Swallow tablets whole.
Common side effects of oxybutynin include dry mouth, constipation, and nausea. Oxybutynin can also cause blurred vision, drowsiness, and dizziness. Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how oxybutynin affects you.
How was your experience with Oxybutynin?
Oxybutynin Cautionary Labels


Uses of Oxybutynin
Oxybutynin is a prescription medication used to treat overactive bladder. Symptoms treated are:
- Painful, frequent urination
- Urination leaking accidents
This medication may be prescribed for other uses. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Oxybutynin Brand Names
Oxybutynin Drug Class
Oxybutynin is part of the drug class:
Side Effects of Oxybutynin
Serious side effects have been reported with oxybutynin. See the "oxybutynin precautions" section. Common side effects of oxybutynin include the following:
Oral (immediate release or XL tablet, liquid):
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
Topical gel:
- Reaction at application site (redness, itching, irritation, pain, rash)
- May also experience side effects listed for the oral formulation
Transdermal:
- Localized redness and swelling, itching
- Diarrhea
- May also experience side effects listed for the oral formulation
This is not a complete list of oxybutynin side effects. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Oxybutynin Interactions
Tell your doctor about all the medications you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- ipratropium oral inhalation (Atrovent HFA), tiotropium oral inhalation (Spiriva HandiHaler)
- potassium chloride (Klor-Con)
- chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton), diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- amitriptyline (Elavil), clomipramine (Anafranil), imipramine (Tofranil)
- Opioid medications such as morphine (MS Contin), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), oxycodone (Oxycontin), methadone (Dolophine), and combination opioid medications such as hydrocodone-acetaminophen (Lorcet, Lortab, Vicodin, Norco), oxycodone-acetaminophen (Endocet, Percocet), and acetaminophen-codeine (Tylenol #3)
- Medications that use the enzyme CYP3A4, such as ketoconazole (Nizoral), itraconazole (Sporanox), miconazole (Lotrimin, Vagistat), erythromycin (E.E.S. granules), clarithromycin (Biaxin)
- Medications that are classified as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, such as donepezil (Aricept), galantamine (Razadyne), and rivastigmine (Exelon)
This is not a complete list of oxybutynin drug interactions. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Oxybutynin Precautions
Serious side effects have been reported with oxybutynin, including the following:
- Central nervous system effects. These may include hallucinations, agitation, confusion, and drowsiness.
- Angioedema. If you experience swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or larynx after taking oxybutynin, call 911 for prompt medical attention.
- Heat prostration. This would include fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating. This can occur if oxybutynin is taken in the presence of high environmental temperature.
Extended release formulation: This formulation has rarely been associated with symptoms of GI obstruction (blockage of stomach or intestines).
Topical gel: To decrease chances of transferring this medication to others, cover treatment area with clothing after gel has dried. Stop using this medication if it causes irritation to the skin. Do not expose this medication to an open flame or smoking until the gel has dried.
Transdermal patch: Remove patch before an MRI.
Oxybutynin can cause drowsiness. Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how oxybutynin affects you.
Do not take oxybutynin if you:
- Are allergic to oxybutynin or to any of its ingredients
- If you have, or are at risk for uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention, gastric retention, or conditions with very decreased gastrointestinal movement
Oxybutynin Food Interactions
Medications can interact with certain foods. In some cases, this may be harmful and your doctor may advise you to avoid certain foods. In the case of oxybutynin, there are no specific foods that you must exclude from your diet while receiving this medication.
Inform MD
Before taking oxybutynin, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions. Especially tell your doctor if you:
- Are allergic to oxybutynin or any of its ingredients
- Have or have had hyperthyroidism, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, hiatal hernia, tachycardia (rapid heart beat), hypertension, myasthenia gravis, and prostatic hypertrophy (enlargement of the prostate gland)
- Have problems with your liver or kidney
- Have a blockage preventing urine flowing out from your bladder
- Have a blockage in your stomach or intestines, or have ulcerative colitis or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Oxybutynin and Pregnancy
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. The FDA categorizes medications based on safety for use during pregnancy. Five categories - A, B, C, D, and X, are used to classify the possible risks to an unborn baby when a medication is taken during pregnancy.
Oxybutynin falls into category B. There are no well-done studies that have been done in humans with oxybutynin. In animal studies, pregnant animals were given this medication, and the babies did not show any medical issues related to this medication.
Oxybutynin and Lactation
Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if oxybutynin crosses into human milk. Because many medications can cross into human milk and because of the possibility for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants with use of this medication, a choice should be made whether to stop nursing or stop the use of this medication. Your doctor will decide if the benefits outweigh the risks of using oxybutynin.
Oxybutynin Usage
Take oxybutynin exactly as prescribed.
Oxybutynin comes in tablet (immediate or extended release), gel, liquid (syrup) or transdermal (patch) form, and is taken up to 4 times daily. It is also available over-the-counter in a patch formulation. This medication can be taken with or without food. Do not chew, divide, or break the extended release form of this medication (ditropan XL tablets). Swallow tablets whole.
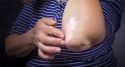
For the topical gel formulation, apply to clean, dry, intact skin on abdomen, thighs, or upper arms/shoulders. Wash hands after use. Cover treated area with clothing after gel has dried to prevent transfer of medication to others. Do not bathe, shower, or swim until 1 hour after gel applied. Do not apply to recently shaved skin.
Oxybutynin Gel 3%: Prior to initial use, press pump 4 times to prime pump; discard any gel dispensed from pump during priming. Rotate application sites to avoid skin irritation.
Oxybutynin Gel 10%: Rotate site; do not apply to same site on consecutive days.
For the transdermal formulation (patch), apply to clean, dry skin on abdomen, hip, or buttock. Select a new site for each new system (avoid reapplication to same site within 7 days). Wear patch under clothing; do not expose to sunlight.
Alcohol may intensify the effect of this medication.
If you miss a dose, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, skipped the missed dose and take your next dose at the regular time. Do not take two doses of oxybutynin at the same time.
Oxybutynin Dosage
Take this medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully.
The dose your doctor recommends may be based on the following:
- the condition being treated
- other medical conditions you have
- other medications you are taking
- how you respond to this medication
- your weight
- your height
- your age
- your gender
Oral (immediate release, extended release)
The recommended dose of oxybutynin for the treatment of overactive bladder is one 5 mg tablet two to three times a day. The maximum recommended dose is one 5 mg tablet four times a day.
The recommended dose of Ditropan XL (oxybutynin chloride) for the treatment of overactive bladder is 5 to 10 mg once daily initially, followed by increases in the dosage by 5 mg at weekly intervals. The maximum recommended dose is 30 mg once daily.
Topical:
The recommended dose of Gelnique 3% (oxybutynin) for the treatment of overactive bladder is 3 pumps (84 mg) once daily. The recommended dose of Gelnique 10% (oxybutynin) for the treatment of overactive bladder is 1 sachet (100 mg/g) once daily.
Transdermal:
The recommended dose of Oxytrol (oxybutynin) is one 3.9 mg/day patch twice weekly (every 3-4 days).
Oxybutynin Overdose
If you take too much oxybutynin, call your healthcare provider or local Poison Control Center, or seek emergency medical attention right away. If oxybutynin is administered by a healthcare provider in a medical setting, it is unlikely that an overdose will occur. However, if an overdose is suspected, seek emergency medical attention.
Other Requirements
Store at 20-25 C.
Protect from light.